- Mall
- Supermarket
- Supplier
- Cross-Border Barter
- Industrial Data
- Warehouse Logistics
- Trade Assurance
- Expo Services
Titanium alloy:
Titanium alloys refer to various alloy metals made of titanium and other metals. Titanium is a homomorphic isomer with a melting point of 1720°C and a close-packed hexagonal crystal lattice structure below 882°C, called a-titanium; above 882°C, it has a body-centered cubic crystal structure, called B-titanium. Taking advantage of the different characteristics of the above two structures of titanium, adding appropriate alloying elements to gradually change its phase transition temperature and phase content to obtain titanium alloys with different structures.
Classification of titanium alloys:
At room temperature, titanium alloys have three matrix structures, and titanium alloys are divided into the following three categories: alpha alloys,(α+β) alloys and beta alloys. China is expressed in TA, TC and TB respectively.

Due to the needs of the development of the aviation industry, the titanium industry has developed at an average annual growth rate of about 8%. The world's annual output of titanium alloy processed materials has reached more than 40,000 tons, and there are nearly 30 titanium alloy brands.
Characteristics of titanium alloy:
Titanium is an important structural metal. Titanium alloys have the characteristics of high strength and small density, good mechanical properties, and good toughness and corrosion resistance.

Processing technology of titanium alloy:
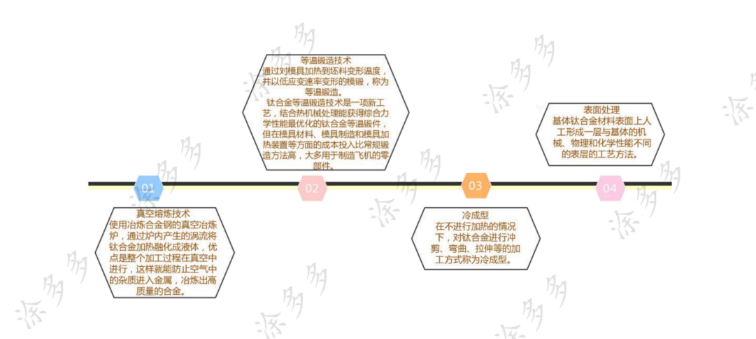
Titanium alloy production waste-residual titanium waste titanium:
Residual titanium and waste titanium come from a wide range of sources. For example, waste titanium produced in the production process of sponge titanium, its upper skin, bottom and sides are stained by impurities such as iron, chlorine, oxygen, nitrogen and other impurities that do not meet product quality standards. These side leather materials and other materials must be processed and recycled; in addition, there are waste titanium produced from titanium ingots, residual titanium (corner residue and titanium chips) produced from processed titanium products, and waste titanium products are important sources.
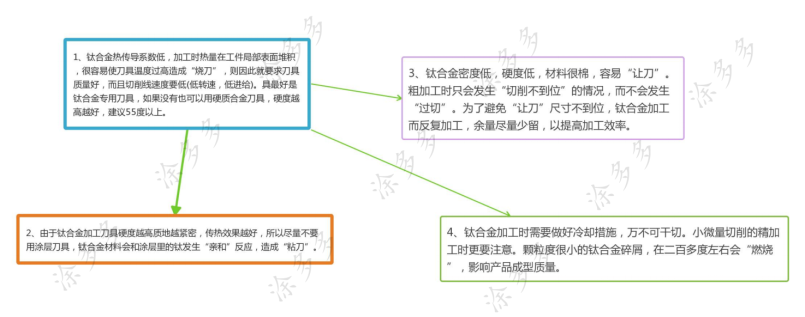
Precautions for titanium alloy processing:
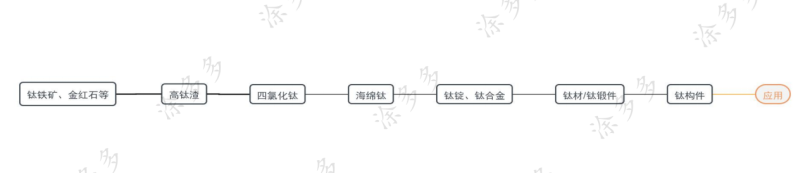
Titanium alloy industry chain:
Titanium alloy melting technology is complex and difficult to process. At present, only four countries in the world, the United States, Russia, Japan, and China, can master complete titanium industry production technology.
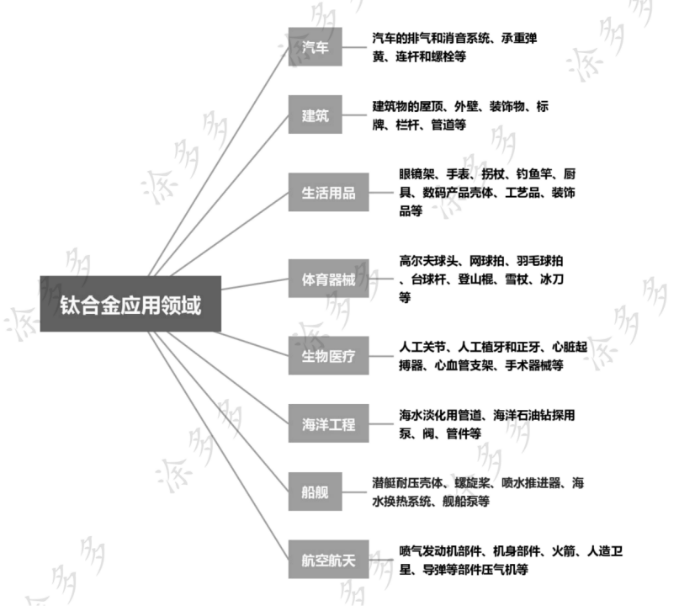
Titanium alloy uses:
Titanium alloys are mainly used to make compressor parts for aircraft engines, followed by structural parts for rockets, missiles and high-speed aircraft. In addition, titanium alloys are also widely used in many fields such as the automobile industry, military equipment, medical care, chemical industry, sporting goods, and daily necessities.
Since the mid-1960s, titanium and its alloys have been used in general industries to make electrodes for the electrolysis industry, condensers for power stations, heaters for petroleum refining and desalination, and environmental pollution control devices. Titanium and its alloys have become a corrosion resistant structural material. In addition, it is also used to produce hydrogen storage materials and shape memory alloys.
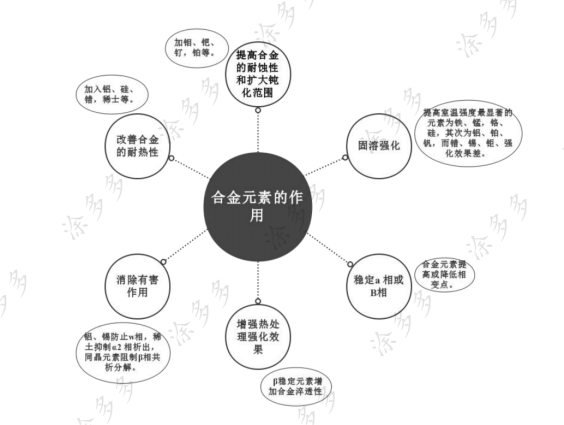
Common alloying elements in titanium alloys and their functions:
The alloying elements commonly added in titanium alloys are aluminum, tin, zirconium, molybdenum, vanadium, chromium, iron, silicon, copper, rare earth, of which the most used is aluminum. The main effects of adding alloying elements are:
China's main titanium alloy manufacturers:
China The companies that can produce higher-end titanium alloy materials in China are mainly Western Superconductor, Baotou, Western Materials, Jintian Titanium Industry, Baowu Special Metallurgical and Tiancheng Aviation Materials.
